A brief history of TFT LCDs:
1957 – John Wallmark of RCA patents the thin film MOSFET.
1992 – Paul K. Weimer of RCA develops Transistor Transistor Technology (TFT) using Wallmark's patents.
1968 – Bernard Lechner of RCA implements TFT technology for the first time in a liquid crystal display (LCD)
1971 - Lechner, FJ Marlowe, EO Nester and J. Tults demonstrate a 2×18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the LCD's dynamic camera mode
1974 – Brody and Fang-Chen Luo demonstrate the first planar active-matrix liquid crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs,
1975 – Brody coined the term "active-matrix LCD,"
2020 - TFT LCD display technology now dominates the display market. It has wiped out the CRT (cathode ray tube) and plasma markets over the past 20 years. The only challenge is OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and Micro LED (maybe still in the lab).
TFT display technology: how does it work?
TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display) technology has a sandwich-like structure with liquid crystal material filled between two glass plates. Two polarizing filters, color filters (RGB, red/green/blue) and two alignment layers determine exactly how much light is allowed to pass and the resulting color.
Each pixel in an active matrix is paired with a transistor that includes a capacitor, enabling each subpixel to retain its charge, rather than needing to send it every time it needs to be changed. The TFT layer controls the flow of light, the color filters reveal the colors, and the top layer houses the visible screen.
TFT LCD structure:
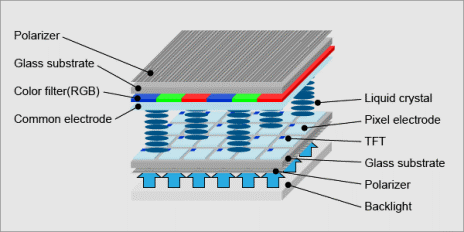
Electric charges are used to cause the liquid crystal material to change its molecular structure, allowing various wavelengths of backlight to "pass through." The active matrix of a TFT display is constantly changing and rapidly changing or refreshing based on the input signal from the controlling device.
The pixels of a TFT display are determined by the color matrix and the underlying density (resolution) of the TFT layout. The more pixels, the more detail is available. Available screen sizes, power consumption, resolutions, interfaces (how to connect) define a TFT display.
The pixels of a TFT display are determined by the color matrix and the underlying density (resolution) of the TFT layout. The more pixels, the more detail is available. Available screen sizes, power consumption, resolutions, interfaces (how to connect) define a TFT display.
A TFT screen by itself cannot emit light like an OLED display, it has to be used with a white bright backlight to produce a picture. Newer panels utilize LED backlights (Light Emitting Diodes) to generate light, so use less power and require less depth for the design.
The TFT display module includes a TFT display screen, an LED backlight and a driving circuit.
Advantages and uses of TFTs
TFT LCDs have several advantages over other types of displays (CRT, plasma). It is light, thin, and energy-efficient, enabling cell phones, laptops, wall-mounted LCD TVs, tablet monitors, and other handheld devices. TFT LCDs are also relatively cheap, making them dominant in the display space.
When we say LCD type, we mean two types of LCDs: active TFT color displays and monochrome passive displays. Before the invention of TFT displays, passive matrix liquid crystal displays were used in the world for many years. Passive matrix LCDs should only be used with monochrome displays such as calculators, watches (not iWatch), thermostats (not Nest), utility meters, etc. Thanks to TFT LCD, the world is more colorful.
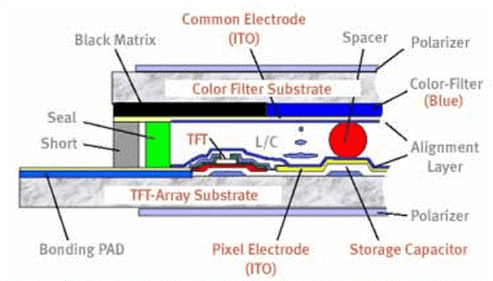
TFT color display:
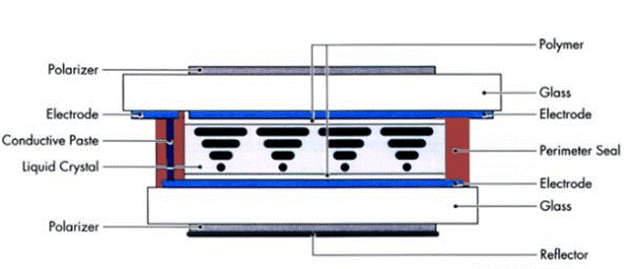
Monochrome passive LCD display:
Want to learn more about TFT displays?
If you want to know more about TFT display technology, please visit our website TFT related information or view our TFT products, if you need further understanding, please feel free to contact us!